Gout is a common but often misunderstood condition, similar to arthritis, marked by sudden and severe joint pain. It’s crucial for those affected and others to grasp this ailment. This guide explains gout and symptoms, helping with early recognition. Identifying these can improve how one manages the condition.
What is Gout and Why Does It Happen?
Gout is caused by uric acid accumulating in the bloodstream. This acid can form sharp crystals in the joints. The reason for this build-up varies. Some people produce too much uric acid, while others don’t remove enough of it through their kidneys. Factors such as eating foods high in purines, drinking alcohol, using diuretics, your family history, and having certain health problems can increase your risk of developing gout. Understanding these factors can help in managing and preventing gout.
When purines are broken down, uric acid is produced. A diet high in purine-rich foods, such as red meat, shellfish, and sugary drinks, can raise uric acid levels. Pair this with alcohol and certain medicines, and the risk of gout increases. But it’s not all about diet. Genetics also play a role. If your family has a history of gout, your chances might be higher. Other health issues, like obesity or diabetes, can also be contributing factors.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Gout
The symptoms of gout are typically intense and come without warning. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
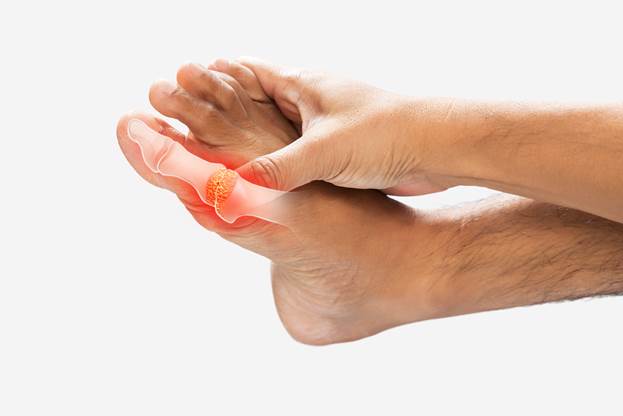
- Severe joint pain: Most often, this pain is in the big toe, but it can occur in other joints like the knees or fingers.
- Redness and swelling: The affected joint appears red and swollen.
- Warmth: The joint may feel warm to the touch.
- Sudden attacks: Gout attacks frequently happen at night and build up quickly.
Identifying elevated uric acid symptoms early can help manage the situation better and prevent the disease from becoming a long-lasting issue. If you notice symptoms such as aching in the joints, this might signal high uric acid levels. Early action is essential.
Stages, Patterns, and Diagnosis of Gout
Gout progresses through several stages if untreated. Initially, it starts with sporadic gout and symptoms also called acute attacks that come and go. Over time, if untreated, these periods of no symptoms become shorter until it develops into a lasting condition known as chronic gout.
Stages of Gout
- Acute Attacks: Sudden sharp pain in one or more joints, often at night.
- Intercritical Gout: Periods of time between attacks when no symptoms appear.
- Chronic Gout: Persistent arthritis with possible development of tophi, which are lumps.
Doctors can diagnose gout by reviewing someone’s medical history, checking uric acid levels in the blood through blood tests, and sometimes analyzing joint fluid. This helps confirm the presence or absence of the needle-like urate crystals.
Managing and Preventing Gout
Addressing lifestyle habits is a big part of managing gout. Adjusting your diet helps significantly. Here’s how you can keep gout in check:
- Diet Changes: Cut down on foods high in purines like red meats and kidney. Include low-fat dairy and lots of fruits.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water daily to help eliminate uric acid.
- Weight Management: Keep a healthy weight to decrease gout flare-ups.
Medications are another key part of managing gout. Short-term options often focus on relief for gout pain, providing quick comfort. Long-term treatments control uric acid symptoms by maintaining low levels in the blood. When seeking the best medicine for high uric acid, a healthcare provider can customize treatment to fit your needs.
The Impact of Gout on Daily Life
Having gout impacts how people live day-to-day. Frequent gout and symptoms can make regular activities hard, affecting quality of life. Finding the right relief for gout pain becomes essential for those affected.
Effects on Daily Activities
- Pain might limit movement, making walking or holding items difficult.
- Recurring attacks can disrupt sleep due to nighttime pain.
- Professional life may be impacted due to missed workdays or less productivity.
Recognizing elevated uric acid symptoms early and seeking medical advice to treat the condition can help lessen these issues. For continued well-being, it’s vital to talk openly with healthcare providers about symptoms and treatment plans.
Myths and Misconceptions About Gout
There are many myths surrounding gout. Some believe it only affects the wealthy or is purely a result of diet. However, these aren’t true. Anyone can develop gout regardless of their financial status or diet. Misunderstandings like these can prevent those affected from seeking timely medical advice and proper care.
Debunking Common Myths
- Myth: Gout is a rich person’s disease.
- Fact: It can affect anyone, not only those with luxurious diets.
- Myth: It’s only the result of eating red meat or drinking alcohol.
- Fact: While diet is a factor, other aspects like genetics and health issues contribute.
Knowing the truth about gout and symptoms encourages better management and can lead to improved treatment outcomes.
Understanding gout and its symptoms of high in uric doesn’t need to be confusing. With knowledge about risk factors, symptoms, and management, controlling gout becomes more accessible. Preventing and managing gout starts with early identification and adopting lifestyle changes. Proper treatment with the best medicine for high uric acid alongside lifestyle adjustments can greatly alleviate the impact on life. For those living with this condition or those just starting to notice high uric symptoms, this guide aims to provide clarity and help on the path toward better management and a healthier lifestyle.