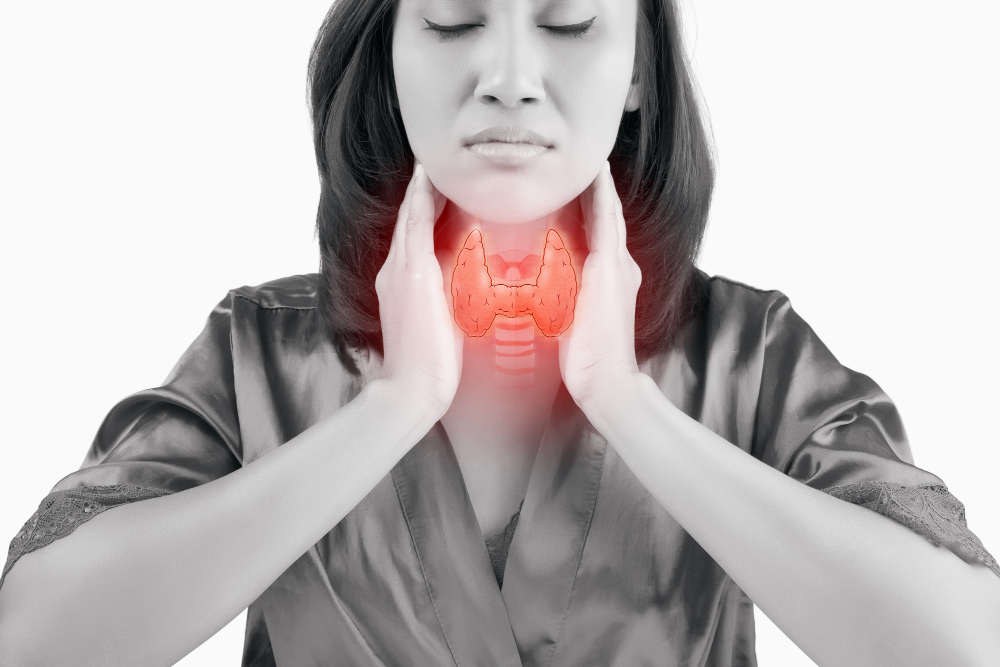
Hyperthyroidism, also known as an overactive thyroid, happens when your thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. This condition can affect your body in many ways. Because the thyroid controls your metabolism, hyperthyroidism can speed up many body processes. Early detection and proper thyroid treatment are important. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), thyroid problems are common worldwide. Understanding hyperthyroidism helps you recognize symptoms and seek help quickly.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism means your thyroid gland works too much. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in your neck. It makes hormones that control how your body uses energy. When the thyroid makes too much hormone, your body speeds up. As a result, you may feel nervous or have a fast heartbeat. Overactive thyroid can affect people of any age, but it is more common in women. Graves’ disease is a leading cause of hyperthyroidism.
Common Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism can cause many symptoms. However, not everyone has all of them. If you notice these signs, talk to your doctor:
Causes and Risk Factors
Several things can cause hyperthyroidism. Some people are more at risk than others. Here are the main causes and risk factors:
How Hyperthyroidism is Diagnosed
Doctors use several steps to diagnose hyperthyroidism. First, they ask about your symptoms and health history. Next, they do a physical exam. Often, they check your neck for swelling or lumps. Then, they order blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels. Sometimes, doctors use imaging tests like ultrasound or a thyroid scan. These tests help find the cause and guide thyroid treatment. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), early diagnosis leads to better outcomes.
Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism
There are several ways to treat hyperthyroidism. The best option depends on your age, health, and the cause of your overactive thyroid. Your doctor will help you choose the right treatment. Common treatments include:
Each treatment has benefits and risks. Therefore, regular follow-up is important to monitor your thyroid hormone levels.
Lifestyle Tips and Prevention
While you cannot always prevent hyperthyroidism, healthy habits can help. Here are some tips to support your thyroid health:
Although these steps cannot always prevent hyperthyroidism, they can help you stay healthy. Early action makes a big difference.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice symptoms of hyperthyroidism, do not wait. For example, if you have a rapid heartbeat, weight loss, or neck swelling, see your doctor soon. Early diagnosis and thyroid treatment can prevent serious problems. In addition, if you have a family history of thyroid disease, regular check-ups are wise. Your doctor can guide you on the best steps for your health.
In summary, hyperthyroidism is a treatable condition, but it requires proper care and attention. For personalized advice and the right treatment plan, consult a healthcare provider at Prabhavati Multy Speciality Hospital & Research Centre. Timely intervention can help you manage the condition effectively.
Contact Prabhavati Multy Speciality Hospital & Research Centre today for expert care and personalized treatment!